UNIT 2: BIochemistry(7 DAYS)
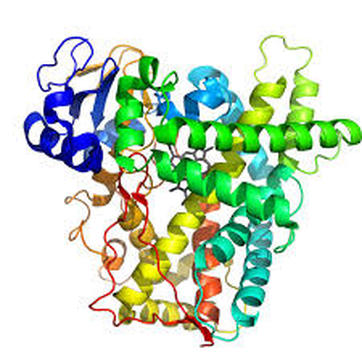
Chemistry and biology overlap heavily, and the field of biochemistry studies the areas in which these two sciences merge. Biochemists study the myriad chemical reactions that occur in living things. The picture is of an important enzyme called cytochrome P-450. Enzymes are nature’s catalysts. They are large protein molecules that act to speed up biochemical reactions in a very specific way. Almost every chemical reaction that occurs in a living organism proceeds with the help of an enzyme that catalyzes only that specific reaction. In this unit, you will get an introduction to the major categories of biomolecules and some of the functions that they serve in living organisms. |
NC STANDARDS
Bio.4.1 Understand how biological molecules are essential to the survival of living organisms.
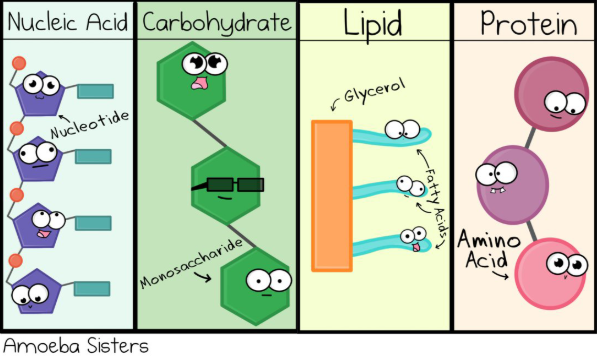
Bio.4.1.1 Compare the structures and functions of the major biological molecules (carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids) as related to the survival of living organisms.
Bio.4.1.2 Summarize the relationship among DNA, proteins and amino acids in carrying out the work of cells and how this is similar in all organisms.
Bio.4.1.3 Explain how enzymes act as catalysts for biological reactions.
Bio.4.1 Understand how biological molecules are essential to the survival of living organisms.
Bio.4.1.1 Compare the structures and functions of the major biological molecules (carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids) as related to the survival of living organisms.
Bio.4.1.2 Summarize the relationship among DNA, proteins and amino acids in carrying out the work of cells and how this is similar in all organisms.
Bio.4.1.3 Explain how enzymes act as catalysts for biological reactions.
ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS
How can I safely conduct a science classroom laboratory investigation?
What are the subunits and functions of the four major groups of organic macromolecules?
In what ways does DNA direct a cell’s activities?
How is DNA responsible for the shape and features of an organism?
How are proteins made in the cell?
How and why do enzymes catalyze biological reactions?
How can I safely conduct a science classroom laboratory investigation?
What are the subunits and functions of the four major groups of organic macromolecules?
In what ways does DNA direct a cell’s activities?
How is DNA responsible for the shape and features of an organism?
How are proteins made in the cell?
How and why do enzymes catalyze biological reactions?
|
DAY 1: CARBON COMPOUNDS
HONORS
Ethanol vs Methanol - Honors DAY 2: BIOMOLECULES
DAY 3: BIOMOLECULES LAB
|
VOCABULARY Macromolecule organic monomer polymer monosaccharide polysaccharide carbohydrate lipid denature catalyst activation energy DNA RNA fatty acid protein amino acid peptide bond nucleic acid nucleotide enzyme substrate carbohydrate protein reactant product |
|
Additional Videos & Review:
Lipids Internet Lesson Proteins Internet Lesson Carbohydrates Internet Lesson |
|
DAY 4: ENZYMES
| enzyme_cutouts.pdf | |
| File Size: | 504 kb |
| File Type: | |
Day 5: ENZYMES LAB
DAY 6: REVIEW
KAHOOT Unit 2 Test Review
Biomolecules GAME
Here are some practice quizzes to help you study for your test.
Biochemistry
Chemistry
Biomolecules GAME
Here are some practice quizzes to help you study for your test.
Biochemistry
Chemistry
DAY 7: UNIT TEST